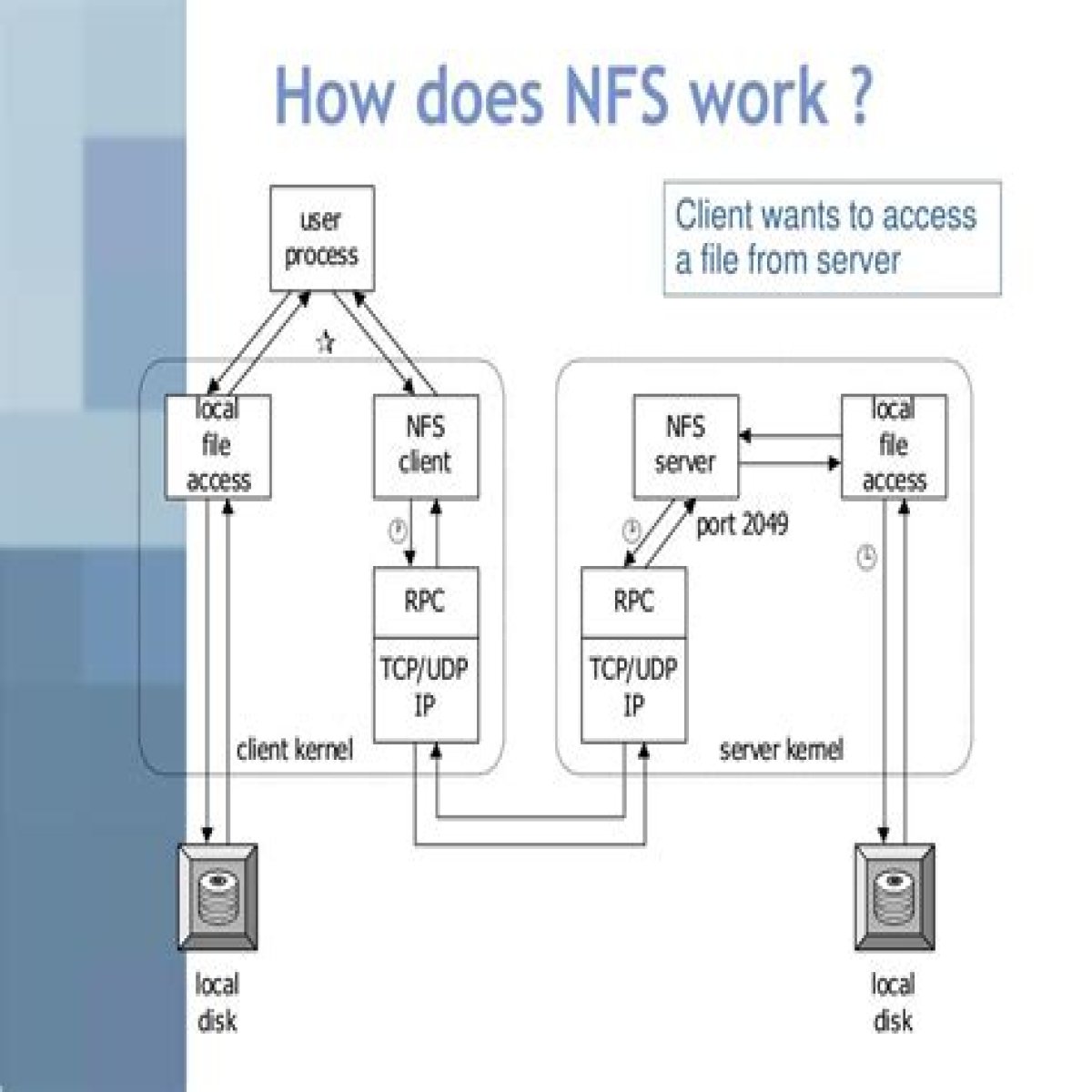
Network File System (NFS) is a distributed file system protocol that allows users to access files over a network as if they were on their local disks. Developed by Sun Microsystems in the 1980s, NFS has become a fundamental technology in networked computing environments, enabling seamless file sharing and remote file access. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of NFS, its architecture, benefits, and how it is used in various applications.
NFS operates on a client-server architecture, where the NFS server hosts the files while the NFS clients access those files over a network. This system is particularly beneficial in environments where multiple users need to access the same data without duplicating files across different machines. As we delve deeper into the topic, we will uncover the technical details that make NFS a robust solution for file sharing.
Whether you are a system administrator, a developer, or just someone interested in technology, understanding NFS is crucial in the context of networked systems. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of NFS, ensuring that you grasp its significance and practical applications in today’s digital landscape.
Table of Contents
What is NFS?
NFS, or Network File System, is a protocol that allows different systems to share files over a network. It enables users to access files on remote computers as if they were on their local machines. This is particularly useful in environments where multiple computers require access to a common set of files.
NFS operates on a client-server model. The NFS server hosts the files, and the NFS clients request access to these files. This architecture allows for efficient file sharing, making it a popular choice among organizations that require centralized data management.
NFS Architecture
The architecture of NFS can be broken down into several key components:
- NFS Server: The server that hosts the files and makes them available to clients.
- NFS Client: Any machine that accesses files from the NFS server.
- Mounting: The process of making a file system available to the NFS client.
- Remote Procedure Calls (RPC): NFS uses RPC to allow clients to communicate with the server.
Client-Server Communication
Communication between the NFS server and client occurs through RPC, which allows the client to send requests to the server for file operations such as reading, writing, or executing files.
File System Mounting
Before a client can access files on an NFS server, it must mount the remote file system. This process involves specifying the server and the directory to mount on the client machine.
Key Features of NFS
NFS comes with several features that enhance its functionality:
- Transparency: Users interact with remote files as if they were local.
- Interoperability: NFS supports multiple operating systems, allowing different systems to share files.
- Scalability: NFS can handle a growing number of clients and file systems.
- Consistency: NFS ensures that all clients have access to the most recent version of a file.
Advantages of NFS
There are numerous advantages to using NFS, including:
- Centralized Management: NFS allows for centralized data storage, simplifying data management.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces the need for duplicate storage of files across multiple machines.
- Ease of Use: Provides a familiar interface for accessing files, improving user experience.
- Flexibility: Supports a wide range of applications and operating systems.
NFS Versions
NFS has gone through several versions since its inception, with each version introducing new features and improvements:
- NFS Version 2: The original version that introduced the basic functionality of NFS.
- NFS Version 3: Added support for larger files and improved performance.
- NFS Version 4: Introduced stateful operations, better security features, and improved performance.
NFS Configuration
Setting up NFS involves several steps:
- Install NFS: Ensure that the NFS server software is installed on the server and the NFS client software on the client machines.
- Configure Exports: Define which directories on the server will be shared in the /etc/exports file.
- Start NFS Services: Start the NFS service on the server and ensure it is running.
- Mount the File System: Use the mount command on the client to access the shared directories.
NFS Security Considerations
While NFS offers numerous benefits, security must be a priority:
- Authentication: Use secure methods for client authentication.
- Encryption: Consider encrypting data to protect sensitive information.
- Access Control: Implement strict access control measures to restrict file access.
Common Use Cases for NFS
NFS is widely used in various environments, including:
- Enterprise Environments: Centralized file storage for large organizations.
- Cloud Storage Solutions: Offering file sharing capabilities in cloud environments.
- Development and Testing: Facilitating access to shared code repositories among developers.
Conclusion
In summary, NFS is a powerful protocol that enables seamless file sharing across networks. Its client-server architecture, combined with its numerous features and advantages, makes it a preferred choice for organizations seeking efficient data management. Understanding how to configure and secure NFS can greatly enhance its effectiveness in various applications.
We encourage you to leave comments or questions regarding NFS and its applications. Additionally, feel free to share this article with others who may find it useful. Explore our site for more articles on technology and network solutions!
Closing Thoughts
Thank you for reading! We hope this article has provided you with valuable insights into NFS and its significance in the world of file sharing. We look forward to seeing you again on our site for more informative content.
Pepperoni Puns: A Slice Of Humor That’s Sure To Make You SmileQuotes Exhausted: Finding Inspiration In Times Of FatigueUnderstanding "Messages Blocked": Causes, Solutions, And Prevention